Blog
How to Calibrate Your Speakers for Optimal Sound Performance
Achieving the best sound quality from your audio system requires more than just buying high-quality speakers. Proper calibration is key to making sure your speakers deliver the full range of sound as intended. Whether you’re setting up a home theater, stereo system, or multi-room audio setup, speaker calibration ensures balanced audio performance, improved clarity, and optimal bass. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to calibrate your speakers for the best sound experience possible.

1. Understand Your Audio Setup
Before diving into the technical aspects of speaker calibration, it’s important to understand the type of audio system you’re working with. Speaker calibration varies depending on whether you’re using a simple stereo system or a more complex surround sound setup.
- Stereo System: Calibration for a stereo system primarily focuses on adjusting the balance between the two speakers for optimal imaging and clarity.
- Surround Sound System: A surround system involves more speakers (center, front left/right, rear, and subwoofer). Calibration here ensures that each speaker works together to create a cohesive soundstage.
2. Choose the Right Listening Position
The position of your speakers—and your listening position—plays a critical role in sound quality. For the best sound performance, your listening position should be in the “sweet spot,” usually at equal distance from all speakers in a surround setup or directly between two stereo speakers.
Stereo Setup:
- Place the speakers at an equal distance from your listening position.
- Form an equilateral triangle where the angle between the two speakers and your listening spot is around 60 degrees.
- Aim the speakers slightly towards the listener for optimal stereo imaging.
Surround Sound Setup:
- The front speakers should be placed at ear level, facing the listening area.
- Surround speakers should be positioned slightly above ear level and behind or to the sides of the listening area.
- The subwoofer should be placed near a wall or in a corner for better bass response, but not directly against the wall to avoid boominess.
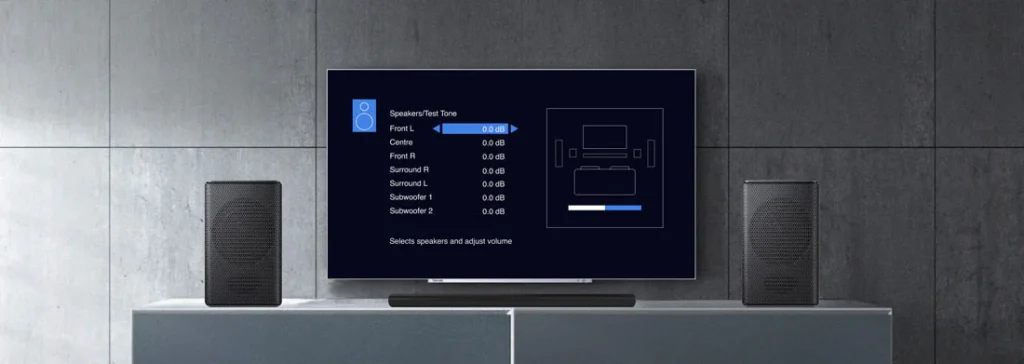
3. Use a Calibration Microphone (For Home Theater Systems)
Most modern AV receivers come with a built-in microphone and automatic speaker calibration tools. These systems analyze the sound in your room and adjust speaker settings to optimize performance. Common systems include Audyssey, YPAO (Yamaha Parametric Room Acoustic Optimizer), and MCACC (Pioneer’s Multi-Channel Acoustic Calibration).
Steps for Auto Calibration:
- Place the Calibration Microphone: Set the microphone at ear level in your primary listening position.
- Activate the Calibration Process: Follow the receiver’s instructions to initiate the auto-calibration. The system will play test tones from each speaker, and the microphone will measure the room’s acoustics.
- Save Settings: Once the calibration is complete, the system will adjust levels, delays, and equalization settings to balance the sound across all speakers.
Manual Calibration (Without a Microphone):
If you don’t have an automatic calibration system, you can calibrate your speakers manually using a sound level meter or a smartphone app like AudioTools or SPL Meter.
- Adjust Volume Levels: Start by setting your receiver’s volume to a reference level (usually 75 dB).
- Test Tones: Play the built-in test tone on your receiver or use a tone generator to send a pink noise signal through each speaker.
- Balance Levels: Adjust the speaker volumes so each speaker produces an equal sound level at the listening position. For surround sound setups, ensure that the front and rear channels are balanced for consistent sound staging.

4. Adjust Speaker Distances (Delay Settings)
Proper speaker distance settings ensure that sound from all speakers reaches the listener at the same time. In a surround sound system, the distance from each speaker to the listening position should be accounted for to avoid timing issues.
To Adjust Speaker Distances:
- Measure Speaker Distances: Use a tape measure to find the exact distance from each speaker to your listening position.
- Input Speaker Distances: Enter these measurements into your AV receiver. Most receivers have an option to manually set speaker distances for each channel.
- Use Delay/Time Alignment: If your receiver doesn’t allow manual input, use the automatic calibration tool mentioned above to adjust the delay settings automatically.
Proper speaker distance settings help ensure that sound from all channels arrives at your ears at the right time, preventing phase issues and ensuring clarity.
5. Tune the Equalizer (EQ) Settings
After setting up speaker distances and levels, fine-tune the sound using the equalizer (EQ) settings on your AV receiver or audio source. The EQ adjusts the frequency response of the speakers, allowing you to enhance bass, midrange, and treble frequencies according to your preference and room acoustics.
EQ Adjustment Tips:
- Bass: If you find the bass too boomy or lacking, adjust the low frequencies. Avoid boosting bass too much, as it can cause distortion, especially at higher volumes.
- Midrange: Adjust the midrange frequencies to balance voices and instruments. If you notice muddiness, slightly reduce the midrange frequencies.
- Treble: If the sound feels dull, increasing treble can help bring out the clarity in vocals and higher-pitched instruments. However, too much treble can result in harshness.
Many audio systems have preset EQ modes, such as “Rock,” “Classical,” or “Movie.” You can experiment with these modes or create a custom setting for the most natural sound in your room.
6. Fine-Tune the Subwoofer
The subwoofer plays a key role in delivering deep bass, but it can sometimes overpower the sound if not calibrated correctly. Too much bass can muddy the sound, while too little can make the audio feel flat.
Subwoofer Placement:
- Positioning: Ideally, place the subwoofer near a wall or in a corner to enhance bass response. Avoid placing it directly in the center of the room or against a wall that might create boomy or uneven bass.
- Adjust Subwoofer Levels: Use the subwoofer’s level control to balance its output with the rest of the speakers. If your system has a bass management feature, ensure that the crossover frequency is set correctly to match the speakers’ capabilities.
- Use Room Correction: If your system has automatic room correction, it will help adjust the subwoofer’s frequency response based on your room’s acoustics.
7. Test and Listen for Clarity
Once all the calibration steps are complete, take time to listen to different types of content (movies, music, games) to ensure that the sound is balanced and clear. Focus on the following:
- Soundstage: Is the sound coming from the correct location (e.g., voices from the center channel, sound effects from the surround speakers)?
- Clarity: Are vocals and dialogue clear? Are there any muddy or overly bright spots in the audio?
- Bass Response: Does the bass sound powerful but not overwhelming?
If anything feels off, don’t hesitate to revisit your settings and make minor adjustments to the EQ, speaker placement, or level balance.

Conclusion
Calibrating your speakers properly is essential to getting the most out of your audio system. Whether you’re using automatic calibration tools, manual adjustments, or both, taking the time to set up your speakers correctly will lead to a more immersive and enjoyable listening experience. By considering speaker placement, distances, levels, and EQ settings, you can create an optimal soundstage that suits your space and preferences. Happy listening!