Blog
Understanding Speaker Impedance and Why It Matters
When setting up an audio system, one of the most important but often overlooked factors is speaker impedance. While it may sound technical, understanding speaker impedance is crucial to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential damage to both your speakers and audio equipment. In this guide, we’ll break down what speaker impedance is, how it affects sound quality, and why it matters when choosing speakers for your system.
What is Speaker Impedance?
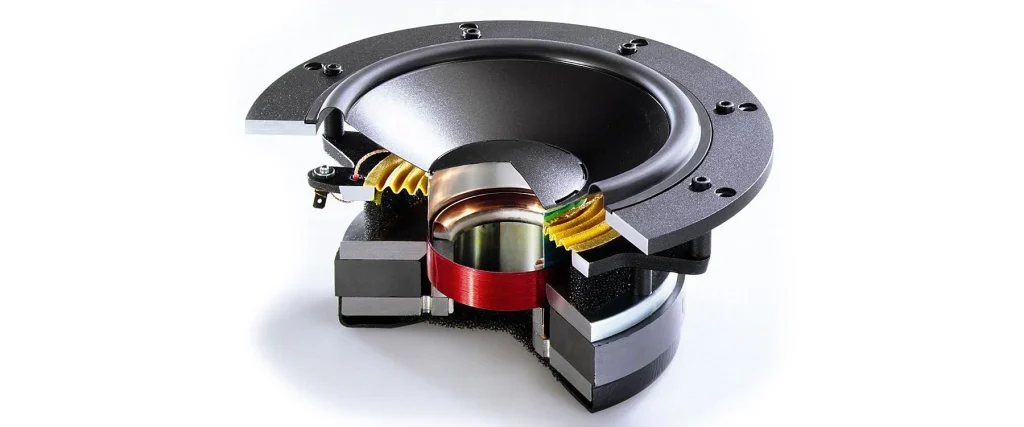
Speaker impedance is a measure of the resistance a speaker presents to the flow of electrical current from an amplifier. It is measured in ohms (Ω), and it essentially indicates how much effort an amplifier needs to make to drive the speaker. The impedance value is important because it determines how easily current flows through the speaker, which in turn affects how efficiently the amplifier can power it.
Types of Impedance
There are two primary categories of speaker impedance:
- Low Impedance: Typically 4 or 6 ohms, these speakers draw more power from an amplifier. They are often used in home theater systems or high-power setups, where more current is needed to produce louder sound.
- High Impedance: Usually 8 ohms, high-impedance speakers are easier on the amplifier, requiring less power to achieve the same sound levels. They are commonly used in home audio systems, where amplifiers are designed to handle them effectively.

How Speaker Impedance Affects Sound Quality
While impedance doesn’t directly affect the tonal quality of a speaker, it plays a crucial role in how well a speaker performs with a given amplifier, which can influence the overall sound experience. Here’s how impedance impacts sound:
1. Power Handling
The impedance of a speaker affects how much power it draws from the amplifier. A lower impedance (e.g., 4 ohms) allows the speaker to draw more power, potentially delivering louder and more dynamic sound. However, this can also put more strain on the amplifier, requiring it to work harder, especially if it’s not designed for low-impedance loads.
In contrast, speakers with higher impedance (e.g., 8 ohms) are more power-efficient and put less load on the amplifier. However, they may not be as capable of reaching the same loudness or dynamic range as a lower-impedance speaker when paired with a similarly powered amplifier.
2. Amplifier Compatibility
Impedance plays a key role in matching speakers with amplifiers. An amplifier is typically designed to drive speakers with a specific impedance rating. If the speaker impedance is too low for the amplifier, the amp may overheat or become damaged due to excessive current draw. If the impedance is too high, the amplifier might not produce enough power to drive the speaker properly, resulting in weaker sound.
For example:
- A 4-ohm speaker requires an amplifier that can supply more power, while an 8-ohm speaker needs less.
- Many modern amplifiers allow you to switch between 4, 6, or 8 ohms to accommodate different speaker impedances.
3. Volume and Loudness
Lower-impedance speakers (e.g., 4 ohms) typically allow more power to flow through them, which can result in higher volumes and better performance at lower amplifier power levels. However, high-impedance speakers (e.g., 8 ohms) generally require more power to reach the same loudness, making them ideal for amplifiers designed to provide higher wattage.
The difference in loudness between 4-ohm and 8-ohm speakers may not be very noticeable at lower volumes, but in large spaces or for high-output setups, the lower-impedance speakers can give you more headroom to achieve high sound levels without distortion.
Why Speaker Impedance Matters
1. Matching Your Amplifier to Your Speaker
One of the main reasons speaker impedance is so important is because it affects the compatibility with your amplifier. If you mismatched the impedance of your speakers and amplifier, it can result in:
- Amplifier Damage: If the speaker impedance is too low for the amplifier, it can cause the amplifier to overheat or burn out due to excessive power draw.
- Poor Sound Performance: A mismatch can lead to distorted sound, weak bass, or lackluster volume, as the amplifier might struggle to drive the speakers properly.
Before purchasing speakers, always check the amplifier’s specifications for the recommended speaker impedance, and choose speakers that match the impedance ratings for optimal performance.
2. Optimizing Sound Performance
Speaker impedance also helps fine-tune your system’s overall sound. If you want to achieve the best audio performance, it’s essential to choose speakers that are well-matched to your amplifier’s power output. Matching the impedance correctly allows the amplifier to work efficiently and deliver the best possible sound with minimal distortion.
If you’re building a home theater or audio system with multiple speakers, ensure that all of the speakers have the same impedance rating to avoid performance imbalances.
3. Customization for Your Setup
Some audio enthusiasts intentionally mix and match speaker impedances to create a unique sound signature. This is more common in advanced audio systems where users combine multiple speakers for surround sound or multi-channel setups. While this can offer more flexibility in tuning the sound, it’s essential to ensure that the speakers and amplifiers are still compatible to prevent damage and ensure even sound distribution.
How to Choose the Right Impedance for Your System
1. Check Your Amplifier’s Impedance Rating
First and foremost, check the specifications of your amplifier. Amplifiers typically support 4, 6, or 8-ohm speakers. Some high-end amplifiers support a wider range of impedances. Make sure the speakers you select are within the range that your amplifier can safely handle.
2. Consider Your Listening Environment
- For Small Rooms: You might not need as much power, so 8-ohm speakers will work fine and reduce strain on your amplifier.
- For Large Rooms or High-Volume Needs: If you plan to fill a large space with sound or push your speakers to high volumes, 4-ohm speakers might be a better fit, as they allow for higher power output.
3. Speaker Type and Purpose
- Home Audio: For general home listening, 8-ohm speakers are usually sufficient and offer good sound quality without stressing the amplifier.
- Home Theater: For home theater systems, especially where powerful surround sound is essential, a mix of speaker impedances may be used, but matching them with the amplifier is crucial.
- Professional Audio: If you’re setting up a live sound or performance system, lower-impedance speakers (4 ohms) are common for their ability to handle more power and reach higher output levels.

Conclusion
Understanding speaker impedance is an essential part of setting up an audio system that performs at its best. It’s not just a technical specification—improper impedance matching can result in poor sound quality or even equipment damage. By considering the impedance of your speakers in relation to your amplifier, room size, and listening preferences, you can ensure that your audio setup delivers clear, powerful sound without overloading your system. Whether you’re building a home theater, a music system, or a professional sound setup, taking the time to choose the right speaker impedance will help you achieve the best listening experience possible.

